EOS
Imágenes médicas

Información general
EOS imaging es una empresa francesa, de alcance mundial de equipamiento médico que desarrolla y comercializa soluciones avanzadas en imágenes para diagnóstico, tratamiento y seguimiento de las patologías musculoesqueléticas más comunes.
La compañía se origina a partir de investigaciones científicas en detección de radiación, galardonada por el Premio Nobel en Física en 1992. Desde allí, diferentes médicos, ingenieros, radiólogos y cirujanos de gran nivel han trabajado en conjunto para transformar esa ciencia en tecnología.
Como resultado, EOS imaging pone a disposición su sistema de imágenes médicas de cuerpo completo y baja radiación (EOS®), workstation 2D/3D (sterEOS®) y un conjunto de soluciones online para planeamiento quirúrgico 3D, para columna, cadera y rodilla (EOSapps).
De esta forma desafía el status quo en imágenes ortopédicas, ofreciendo precisión 2D y 3D a una baja dosis y fomentando un nuevo estándar de tratamiento, específico para cada paciente.
La plataforma EOS® es una combinación única de tecnología en imágenes de baja dosis 2D/3D, software y servicios que agregan valor a cada etapa de la atención del paciente con patología musculoesquelética, desde el diagnóstico hasta el seguimiento a largo plazo.
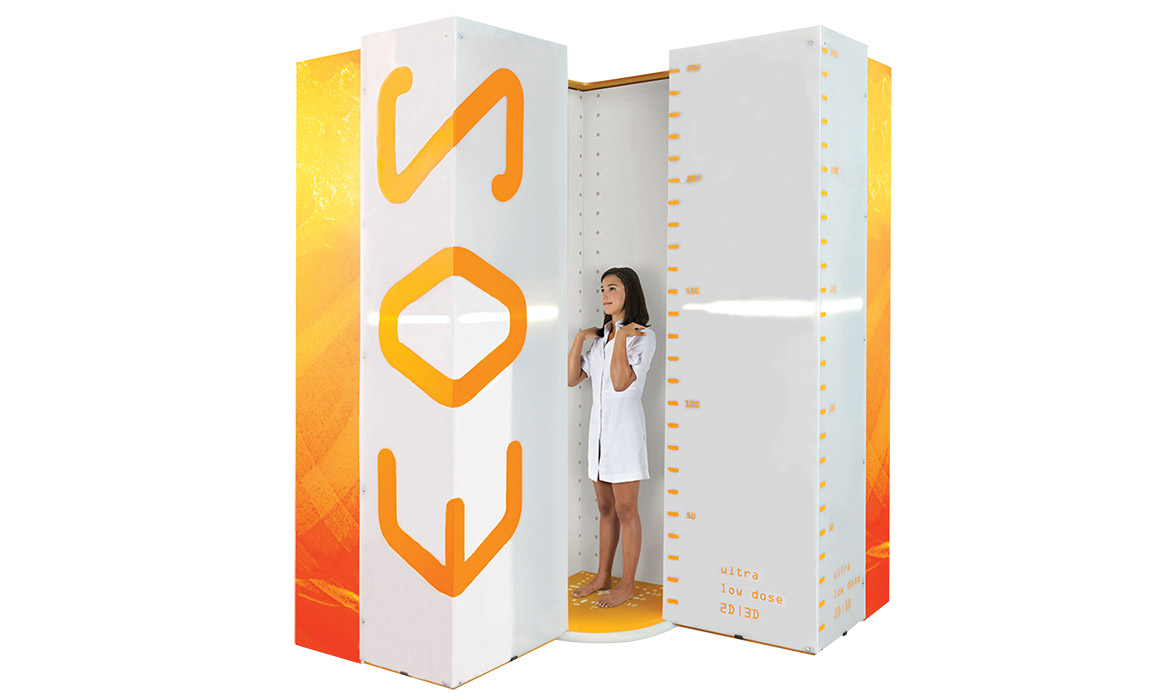
EOS permite realizar un estudio de cuerpo completo con baja dosis (Micro Dose), obteniendo de esta forma imágenes estéreo-radiográficas en bipedestación, es decir, con el paciente soportando su propio peso. Dos imágenes, una frontal y otra lateral, son adquiridas en simultáneo en menos de 20 segundos, sin ningún tipo de distorsión.
La Workstation que acompaña al equipo, sterEOS®, permite crear modelos 3D específicos para cada paciente, calcular más de 100 parámetros clínicos automáticamente y generar reportes personalizados.
También ofrece servicios 3D online y aplicaciones basadas en la nube (disponibilidad según la región) para planificación de cirugías.
Beneficios del sistema EOS®
- Imágenes con baja dosis de radiación: la dosis de radiación es 50% menor comparada con sistemas DR, 85% menor comparada con un sistema CR y un 95% menor que en un escaneo por CT clásico. La opción Micro Dose emplea una dosis equivalente a la radiación natural de una semana.
- Permite obtener imágenes de cuerpo completo, evaluando las articulaciones como un sistema global y bajo el efecto del peso propio del cuerpo, obteniendo un mejor diagnóstico.
- Las imágenes no sufren magnificación ni distorsiones, asegurando mediciones precisas.
- Excelente contraste, con más de 65000 niveles de grises para una alta calidad de imagen.
- Alto rendimiento: rápidas adquisiciones de imágenes del cuerpo completo. En adultos, menos de 20 segundos, y en pediátricos menos de 15 segundos. Esto permite un ciclo de examen eficiente, de alrededor de 4 minutos, aún para casos complejos de columna y cuerpo completo.
Beneficios vinculados a la Workstation:
- Set de datos y modelo 3D, en posición funcional, para una evaluación global del sistema esquelético de cada paciente.
- Cálculo automático de parámetros clínicos 3D para un tratamiento preciso y planificación de cirugías.
- Permite exportar imágenes, reportes de paciente y modelos 3D al PACS.
Flujo de trabajo de modelado 3D rápido y directo, dedicado a la evaluación postural, columna, pelvis, miembros inferiores y Artroplastia Total de Cadera. - Vinculación directa con servicios 3D y EOSapps, plataformas 3D de panificación de cirugías. El conjunto de datos 3D particulares para cada paciente permite planificar procedimientos de colocación de implantes en 3D con EOSapps.
- Mejor comprensión del posicionamiento, rotación y orientación de los huesos.
- Seguimiento de patologías pediátricas con Micro Dose.
Áreas de aplicación
Servicio de Diagnóstico por Imágenes
Traumatología y Ortopedia
- Diagnóstico
- Seguimiento de patologías musculoesqueléticas
- Planificación de cirugías
- Seguimiento post quirúrgico
Centros de referencia
- Contactarse con un asesor para conocer algunos centros de referencia en la región.
Publicaciones Científicas
New EOS Imaging Protocol Allows a Substantial Reduction in Radiation Exposure for Scoliosis Patients
Although statistically significant differences in average measurement error were observed in lordosis and lumbar apex
rotation, these differences are not believed to be clinically significant.

Three-dimensional EOS Analysis of Apical Vertebral Rotation in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
The present study is the first study to measure AVR in a large population of AIS patients using EOS 3-dimensional reconstruction. We report the correction magnitude was significantly affected by the construct.

Flexibility analysis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis on side-bendingimages using the EOS imaging system
The standing side-bending images in the EOS device contributed the same results as thesupine images, with five times less irradiation. They should therefore be used in clinical routine.

Radiography of scoliosis: Comparative doselevels and image quality between a dynamicflat-panel detector and a slot-scanningdevice (EOS system)
For scoliosis evaluation, the SSS, compared to the DFD system, offers enhancedimage quality while reducing the entrance skin dose in the most radiosensitive areas.
Descargar
EOS microdose protocol for the radiological follow-up of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
Results of the current study show that the new microdose acquisition protocol can be used in clinical practice without altering the quality of the images. The resulting radiation exposure was 5.5
times lower than that received with the prior protocol.

A radiolucent chair for sitting-posture radiographs in non-ambulatory children: use in biplanar digital slot-scanning
EOS imaging enables fast 2-D/3-D imaging of children in standing
load-bearing position. Non-ambulatory children with neuromuscular scoliosis need evaluation of their spinal balance
while in a normal daily position.

Three-Dimensional Spinal Morphology Can Differentiate Between Progressive and Nonprogressive Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis at the Initial Presentation
This study confi rms that even at the initial visit, 3D morphological differences exist between P and NP AIS. It supports the use of 3D reconstructions of the spine in the initial evaluation of AIS to help predict outcome.

Ionizing radiation doses during lower limb torsion and anteversion measurements by EOS stereoradiography and computed tomography
The SR system delivered substantially lower doses of ionizing radiation doses than CT to all the organs studied: CT doses were 4.1 times higher to the ovaries, 24 times higher for the testicles, and
13–30 times higher for the knees and ankles.

Measuring femoral and rotational alignment: EOSsystem versus computed tomography
Femoral torsion was 13.4◦by EOS vs. 13.7◦by CT (P = 0.5) and tibial torsion was 30.8◦by EOS vs. 30.3◦by CT (P = 0.4). Strong associations were found between EOS and CT valuesfor both femoral torsion (P = 0.93) and tibial torsion (P = 0.89).
Descargar
EOS Low-Dose Radiography: A Reliable and Accurate Upright Assessment of Lower-Limb Lengths
Upright EOS protocols that utilize a faster speed and lower current are more accurate than CT scanograms and conventional radiographs for the assessment of length and also are associated with a significantly lower radiation exposure.
Descargar
Comparison of radiation dose, workflow, patient comfort and financial break-even of standard digital radiography and a novel biplanar low-dose X-ray system for upright full-length lower limb and whole spine radiography
The biplanar X-ray unit reduces radiation exposure and increases subjective noise exposure to patients.

3D analysis of brace treatment in idiopathic scoliosis
The Cobb angle was significantly improved. It also showed a significant hypolordotic effect. However, the results showed a high variability of the brace treatment effect in almost every parameter.

Musculoskeletal imaging in progress: The EOS imaging system
Further technological improvements might result in other clinical
indications of EOS imaging, namely a better sensibility to skeletal structure changes.

The EOS™ imaging system and its uses in daily orthopaedic practice
In this mini-review, general principles and uses of this groundbreaking integrated orthopaedic solution is reviewed with a few highlighted examples from our own clinical practice.

Diagnostic Imaging of Spinal Deformities
We established that the EOS system offers overall enhanced image quality while reducing drastically the entrance dose for the patient.

Know-how in osteoarticular radiology
Recent developments in 3D modeling of the lower limbs offer new perspectives, especially for total arthroplasties of the hip and knee. A complete 3D evaluation of the weight-bearing legs is now possible on a routine basis and with very low radiation doses.
Descargar
3D evaluation of surgical correction of idiopathic scoliosis by vertebral column manipulation
EOS and sterEOS allowed both a 2D and a 3D evaluation of the
correction of this idiopathic scoliosis using the vertebral column
manipulation (VCM) method.

Degenerative scoliosis / hyperrotatory paradox kyphosis
EOS, and sterEOS, specifically provided a unique opportunity to visualize in both 2D and 3D this severe spinal deformity and quantitatively evaluate the degree of spinal deformation, sagittal imbalance and decompensation.

Analysis of implant positioning after total hip arthroplasty dislocation using the EOS® system : a case report
The EOS system provides a comprehensive analysis of component orientation in standing and sitting positions after THA and may allow surgeons to better understand, and thus prevent, cases of post-THA dislocation.

Dose and Image Quality
EOS is an innovative digital imaging system, allowing long length,
simultaneously acquired frontal and lateral images all at up to 9.2
times lower dosage than a conventional CR system.

Degenerative Scoliosis in the elderly
The various 3D viewsoffered by the sterEOS 3D modeling allowed better visualization of the disease. The 3D modeling helped quantify the spinal degeneration of the patient, while also helping the physician confirm the results of his therapy decision.
Descargar
Clinical Case: 3D evaluation of surgical correction of idiopathic scoliosis by vertebral column manipulation
EOS and sterEOS allowed both a 2D and a 3D evaluation of the correction of this idiopathic scoliosis using the vertebral column manipulation (VCM) method. sterEOS 3D reconstruction enabled the physician to highlight the correction of the scoliosis in the three directions.

Clinical Case: Degenerative scoliosis / hyperrotatory paradox kyphosis
EOS and sterEOS specifically provided a unique opportunity to visualize in both 2D and 3D this severe spinal deformity and quantitatively evaluate the degree of spinal deformation, sagittal imbalance and decompensation.
Descargar
Clinical Case : Medial femorotibial osteoarthritis and genu-valgum: Where is the problem?
The measurement of the coronal alignment of the knee plays a major role in the planning of total knee arthroplasty or osteotomy realignment. The case we report here illustrates the limitations of conventional 2D measurement.
Descargar
Clinical Case: Image Quality
Scoliosis patients often require repeated X-ray exposure, which is why this population deserves particular attention and became the focus of this initial dose reduction study. Obtaining good quality diagnostic images with a significantly lower dose of radiation is an important public health goal, especially for these patients.

Clinical Case: Degenerative Scoliosis in the elderly
In conclusion, this particular patient benefited greatly by having his exams performed using EOS. Not only was his physician able to obtain long length, weight-bearing X-ray images, important in observing overall balance and posture, but the various 3D views offered by the sterEOS 3D modeling allowed better visualization of the disease.
Descargar
Angle Measurement Reproducibility Using EOS
Reproducibilidad de medición de ángulo con EOS. Reconstrucciones tridimensionales en adolescentes. Escoliosis idiopática tratada por instrumentación posterior.
Descargar
Rayos x, Dosis baja, cuerpo completo. Chequeos de salud
EOS® es un sistema de imágenes de rayos X de baja dosis que proporciona imágenes de alta calidad que soportan peso gracias a la combinación de una tecnología de escaneo de ranura y adquisición simultánea de frontal e imágenes laterales.
Descargar



